Advertisement
Advertisement
Asian stocks draw massive foreign inflows on softer dollar, growth optimism
By:
By Gaurav Dogra (Reuters) - Emerging Asia ex-China stocks received massive inflows in January, with investors expecting the U.S. Federal Reserve to slow down the pace of its rate hikes and as the dollar weakened against regional currencies.
By Gaurav Dogra
(Reuters) – Emerging Asia ex-China stocks received massive inflows in January, with investors expecting the U.S. Federal Reserve to slow down the pace of its rate hikes and as the dollar weakened against regional currencies.
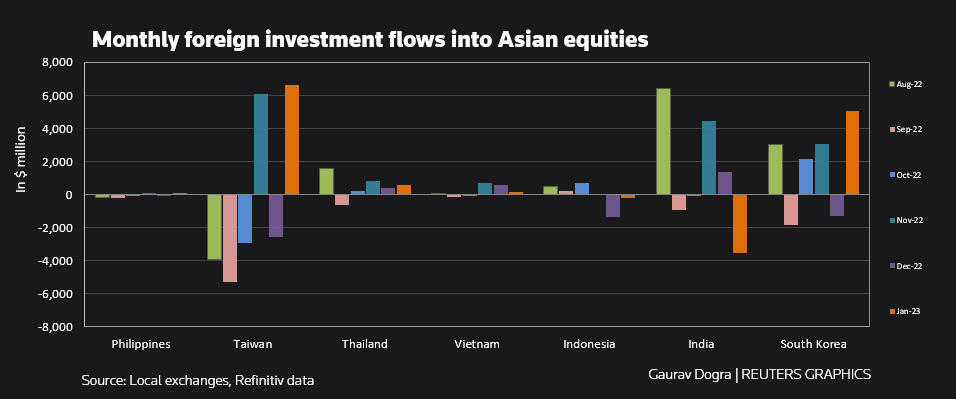
Data from stock exchanges in Taiwan, India, the Philippines, Vietnam, Thailand, Indonesia and South Korea showed that foreigners purchased a net $8.8 billion worth of regional equities in January. They had sold $57.2 billion in regional equities last year.
Also, China’s decision to reopen its borders fuelled hopes that the region’s factory activity and exports would be more potent this year, aiding their profits.
Taiwan and South Korea witnessed their biggest monthly purchases in at least two years, with net inflows amounting to about $6.6 billion and $5 billion, respectively.
“Brewing expectations of an impending end to the Fed’s rate-hike cycle are providing some support for rate-sensitive growth sectors,” said Yeap Jun Rong, a market strategist at IG.
“That may account for the strong inflows in Taiwan and South Korea, which are more growth-exposed.”
Meanwhile, equity markets in Thailand, Vietnam and the Philippines also received $565 million, $178 million and $122 million worth of foreign money, respectively.
Indian equities witnessed $3.52 billion worth of outflows due to higher valuations and the fallout from the slump in Adani Group stocks.
The MSCI Asia-Pacific has gained 7.2% this year after declining about 20% in 2022. The index’s forward 12-month price-to-earnings ratio stood at 13.24 at the end of January, still below the 10-year average of 13.44.
Aman Patel, an investment strategist at Credit Suisse, said slowing economic growth coupled with high input costs put revenue and margins of regional firms at risk, which could trigger the next leg lower in broad equities.
However, he expects divergent performance as China’s post-zero-COVID-policy re-rating is likely to continue as valuations are still near the long-term average.
“The release of domestic demand has the capacity to drive growth higher despite still weak external demand,” he said.
(Reporting by Gaurav Dogra and Patturaja Murugaboopathy in Bengaluru; Editing by Sherry Jacob-Phillips)
About the Author
Reuterscontributor
Reuters, the news and media division of Thomson Reuters, is the world’s largest international multimedia news provider reaching more than one billion people every day. Reuters provides trusted business, financial, national, and international news to professionals via Thomson Reuters desktops, the world's media organizations, and directly to consumers at Reuters.com and via Reuters TV. Learn more about Thomson Reuters products:
Latest news and analysis
Advertisement
